使用Paddle-TensorRT库预测¶
NVIDIA TensorRT 是一个高性能的深度学习预测库,可为深度学习推理应用程序提供低延迟和高吞吐量。PaddlePaddle 采用了子图的形式对TensorRT进行了集成,即我们可以使用该模块来提升Paddle模型的预测性能。该模块依旧在持续开发中,目前已支持的模型有:AlexNet, MobileNetV1, ResNet50, VGG19, ResNext, Se-ReNext, GoogLeNet, DPN, ICNET, Deeplabv3, MobileNet-SSD等。在这篇文档中,我们将会对Paddle-TensorRT库的获取、使用和原理进行介绍。
内容¶
编译Paddle-TRT预测库¶
使用Docker编译预测库
TensorRT预测库目前仅支持使用GPU编译。
下载Paddle
git clone https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/Paddle.git
获取docker镜像
nvidia-docker run --name paddle_trt -v $PWD/Paddle:/Paddle -it hub.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddle:latest-dev /bin/bash
编译Paddle TensorRT
# 在docker容器中执行以下操作 cd /Paddle mkdir build cd build # TENSORRT_ROOT为TRT的路径,默认为 /usr,根据自己需求进行改动 # MKLDNN 可以根据自己的需求自行打开 cmake .. \ -DWITH_FLUID_ONLY=ON \ -DWITH_MKL=ON \ -DWITH_MKLDNN=OFF \ -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release \ -DWITH_PYTHON=OFF \ -DTENSORRT_ROOT=/usr \ -DON_INFER=ON # 编译 make -j # 生成预测库 make inference_lib_dist -j
编译后的库的目录如下:
fluid_inference_install_dir ├── paddle │ ├── CMakeCache.txt ├── version.txt ├── third_party ├── boost ├── install └── engine3fluid_inference_install_dir下, paddle目录包含了预测库的头文件和预测库的lib, version.txt 中包含了lib的版本和配置信息,third_party 中包含了预测库依赖的第三方库
Paddle-TRT接口使用¶
Paddle-TRT预测使用总体上分为以下步骤:
- 创建合适的配置AnalysisConfig.
- 根据配置创建
PaddlePredictor. - 创建输入tensor.
- 获取输出tensor,输出结果.
以下的代码展示了完整的过程:
#include "paddle_inference_api.h"
namespace paddle {
using paddle::AnalysisConfig;
void RunTensorRT(int batch_size, std::string model_dirname) {
// 1. 创建AnalysisConfig
AnalysisConfig config(model_dirname);
// config->SetModel(model_dirname + "/model",
// model_dirname + "/params");
config->EnableUseGpu(10, 0 /*gpu_id*/);
// 我们在这里使用了 ZeroCopyTensor, 因此需要将此设置成false
config->SwitchUseFeedFetchOps(false);
config->EnableTensorRtEngine(1 << 20 /*work_space_size*/, batch_size /*max_batch_size*/, AnalysisConfig::Precision::kFloat32, false /*use_static*/);
// 2. 根据config 创建predictor
auto predictor = CreatePaddlePredictor(config);
// 3. 创建输入 tensor
int channels = 3;
int height = 224;
int width = 224;
float *input = new float[input_num];
memset(input, 0, input_num * sizeof(float));
auto input_names = predictor->GetInputNames();
auto input_t = predictor->GetInputTensor(input_names[0]);
input_t->Reshape({batch_size, channels, height, width});
input_t->copy_from_cpu(input);
// 4. 运行
predictor->ZeroCopyRun()
// 5. 获取输出
std::vector<float> out_data;
auto output_names = predictor->GetOutputNames();
auto output_t = predictor->GetOutputTensor(output_names[0]);
std::vector<int> output_shape = output_t->shape();
int out_num = std::accumulate(output_shape.begin(), output_shape.end(), 1, std::multiplies<int>());
out_data.resize(out_num);
output_t->copy_to_cpu(out_data.data());
}
} // namespace paddle
int main() {
// 模型下载地址 http://paddle-inference-dist.cdn.bcebos.com/tensorrt_test/mobilenet.tar.gz
paddle::RunTensorRT(1, "./mobilenet");
return 0;
}
Paddle-TRT参数介绍¶
在使用AnalysisPredictor时,我们通过配置
config->EnableTensorRtEngine(1 << 20 /* workspace_size*/,
batch_size /*max_batch_size*/,
3 /*min_subgraph_size*/,
AnalysisConfig::Precision::kFloat32 /*precision*/,
false /*use_static*/,
false /* use_calib_mode*/);
的方式来指定使用Paddle-TRT子图方式来运行。以下我们将对此接口中的参数进行详细的介绍:
workspace_size,类型:int,默认值为1 << 20。max_batch_size,类型:int,默认值1。需要提前设置最大的batch的大小,运行时batch数目不得超过此大小。min_subgraph_size,类型:int,默认值3。Paddle-TRT是以子图的形式运行,为了避免性能损失,当子图内部节点个数大于min_subgraph_size的时候,才会使用Paddle-TRT运行。precision,类型:enum class Precision {kFloat32 = 0, kInt8,};, 默认值为AnalysisConfig::Precision::kFloat32。如果需要使用Paddle-TRT calib int8的时候,需要指定precision为AnalysisConfig::Precision::kInt8, 且use_calib_mode为trueuse_static,类型:bool, 默认值为false。如果指定为true,在初次运行程序的时候会将TRT的优化信息进行序列化,下次运行的时候直接加载优化的序列化信息而不需要重新生成。use_calib_mode,类型:bool, 默认值为false。如果需要运行Paddle-TRT calib int8的时候,需要将此设置为true。
Note: Paddle-TRT目前只支持固定shape的输入,不支持变化shape的输入。
Paddle-TRT样例编译测试¶
下载样例
https://paddle-inference-dist.cdn.bcebos.com/tensorrt_test/paddle_trt_samples_v1.5.tar.gz
解压后的目录如下:
sample ├── CMakeLists.txt ├── mobilenet_test.cc ├── thread_mobilenet_test.cc ├── mobilenetv1 │ ├── model │ └── params └── run_impl.sh
mobilenet_test.cc为单线程的程序文件thread_mobilenet_test.cc为多线程的程序文件mobilenetv1为模型文件
在这里假设预测库的路径为
BASE_DIR/fluid_inference_install_dir/,样例所在的目录为SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample编译样例
cd SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample # sh run_impl.sh {预测库的地址} {测试脚本的名字} {模型目录} sh run_impl.sh BASE_DIR/fluid_inference_install_dir/ mobilenet_test SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample/mobilenetv1
编译多线程的样例
cd SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample # sh run_impl.sh {预测库的地址} {测试脚本的名字} {模型目录} sh run_impl.sh BASE_DIR/fluid_inference_install_dir/ thread_mobilenet_test SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample/mobilenetv1
Paddle-TRT INT8使用¶
Paddle-TRT INT8 简介
神经网络的参数在一定程度上是冗余的,在很多任务上,我们可以在保证模型精度的前提下,将Float32的模型转换成Int8的模型。目前,Paddle-TRT支持离线将预训练好的Float32模型转换成Int8的模型,具体的流程如下:1)生成校准表(Calibration table);我们准备500张左右的真实输入数据,并将数据输入到模型中去,Paddle-TRT会统计模型中每个op输入和输出值的范围信息,并将记录到校准表中,这些信息有效的减少了模型转换时的信息损失。2)生成校准表后,再次运行模型,Paddle-TRT会自动加载校准表,并进行INT8模式下的预测。编译测试INT8样例
cd SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample # sh run_impl.sh {预测库的地址} {测试脚本的名字} {模型目录} # 我们随机生成了500个输入来模拟这一过程,建议大家用真实样例进行实验。 sh run_impl.sh BASE_DIR/fluid_inference_install_dir/ fluid_generate_calib_test SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample/mobilenetv1
运行结束后,在
SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample/build/mobilenetv1/_opt_cache模型目录下会多出一个名字为trt_calib_*的文件,即校准表。# 执行INT8预测 # 将带校准表的模型文件拷贝到特定地址 cp -rf SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample/build/mobilenetv1 SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample/mobilenetv1_calib sh run_impl.sh BASE_DIR/fluid_inference_install_dir/ fluid_int8_test SAMPLE_BASE_DIR/sample/mobilenetv1_calib
Paddle-TRT子图运行原理¶
PaddlePaddle采用子图的形式对TensorRT进行集成,当模型加载后,神经网络可以表示为由变量和运算节点组成的计算图。Paddle TensorRT实现的功能是能够对整个图进行扫描,发现图中可以使用TensorRT优化的子图,并使用TensorRT节点替换它们。在模型的推断期间,如果遇到TensorRT节点,Paddle会调用TensoRT库对该节点进行优化,其他的节点调用Paddle的原生实现。TensorRT在推断期间能够进行Op的横向和纵向融合,过滤掉冗余的Op,并对特定平台下的特定的Op选择合适的kenel等进行优化,能够加快模型的预测速度。
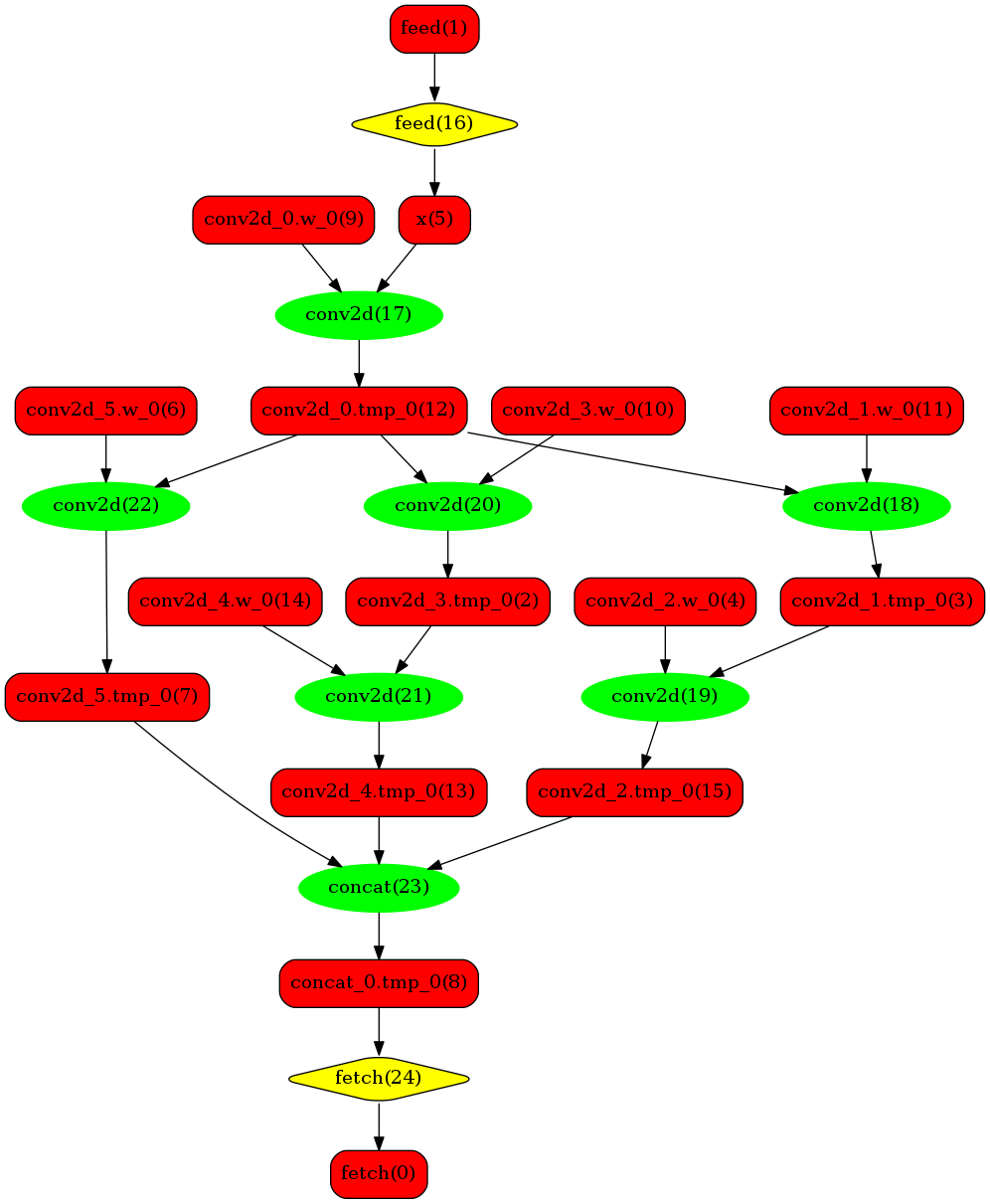
下图使用一个简单的模型展示了这个过程:
原始网络
转换的网络
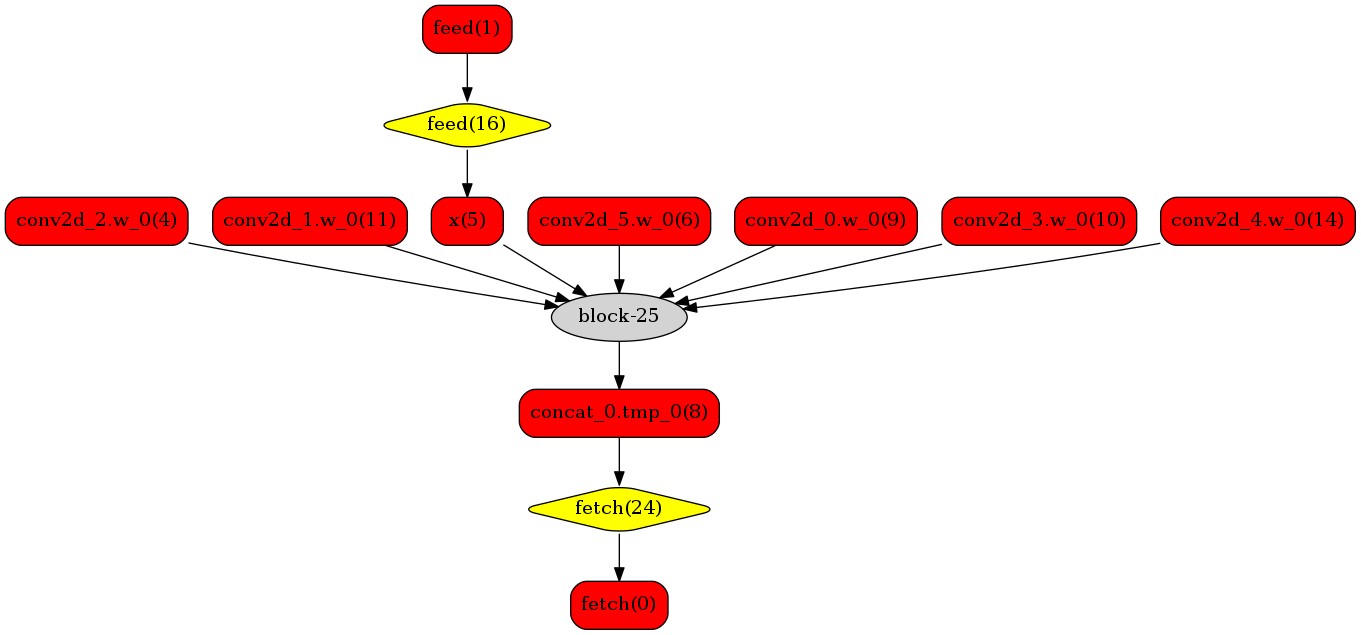
我们可以在原始模型网络中看到,绿色节点表示可以被TensorRT支持的节点,红色节点表示网络中的变量,黄色表示Paddle只能被Paddle原生实现执行的节点。那些在原始网络中的绿色节点被提取出来汇集成子图,并由一个TensorRT节点代替,成为转换网络中的block-25 节点。在网络运行过程中,如果遇到该节点,Paddle将调用TensorRT库来对其执行。
